Optical Line Terminal (OLT): The Core Engine of Passive Optical LANs
Release Time : 2025-10-10
In today's era of sweeping digitalization, scenarios like campuses, hotels, and enterprise LANs are increasingly in need of high-speed, stable, and efficient networks. As the core device of passive optical LANs (POLs), the optical line terminal (OLT) is like the heart of the network world, providing powerful and reliable support for network deployment in various scenarios and becoming crucial for meeting diverse network needs.
Adapting to Diverse Scenarios and Flexibly Building POL Networks
With its exceptional adaptability, the OLT is widely applicable to OLT deployment in various environments, including campuses, hotels, and enterprise LANs. Whether it's a vibrant campus that needs to meet the diverse network needs of teachers and students for teaching, research, and entertainment; a warm and comfortable hotel that provides guests with smooth online services and a convenient smart experience; or an efficient enterprise LAN that ensures internal communications and efficient business operations, the OLT can handle it with ease.
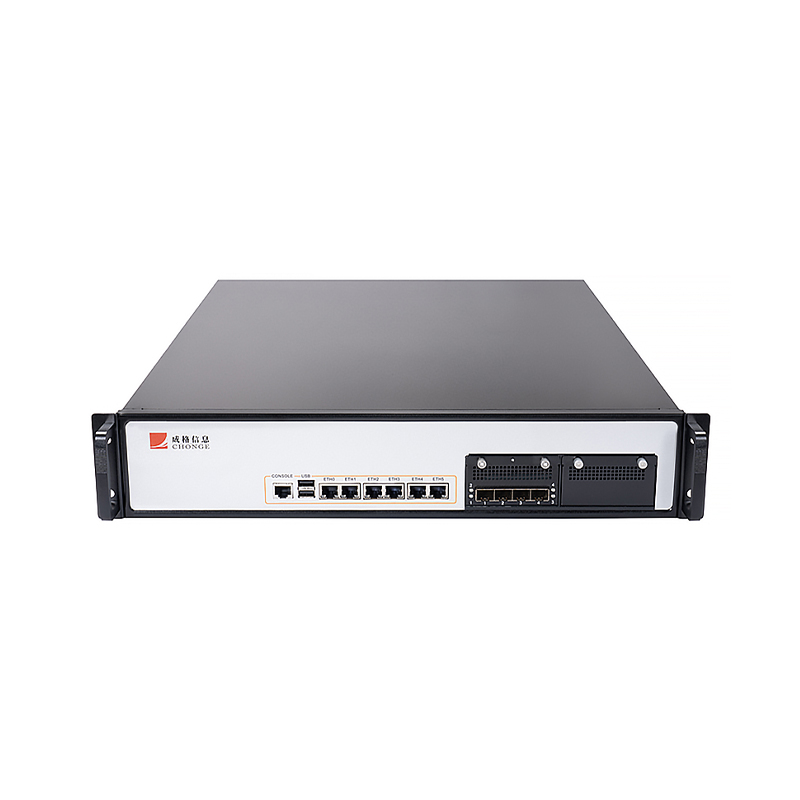
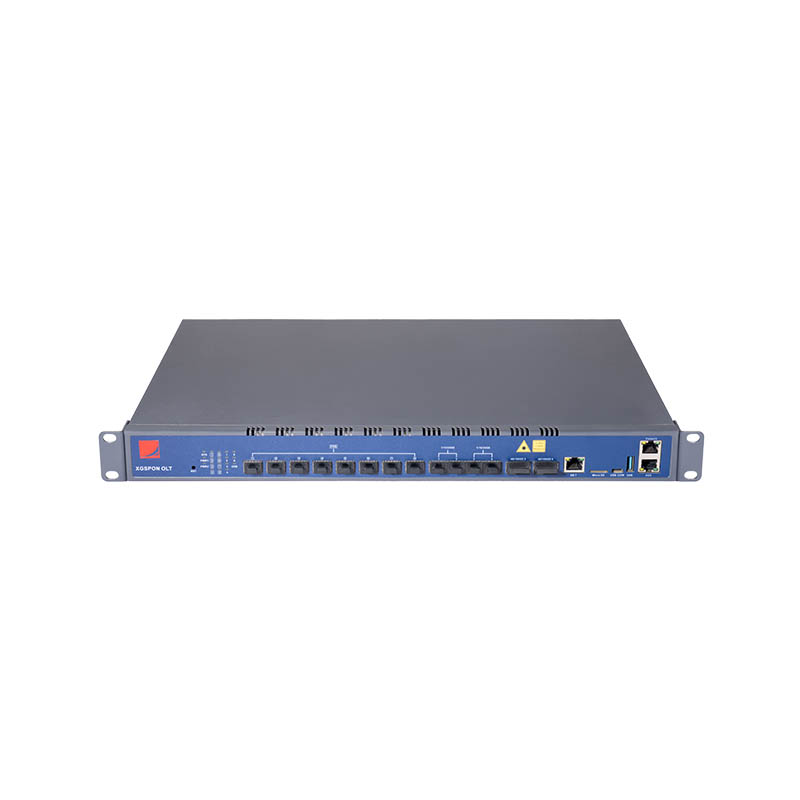
It supports GPON/XG(s) PON technology, providing users with a variety of options. Available in both cassette and rack-mount form factors, this flexible design allows customers to tailor their POL networking solutions to their specific needs, such as site size, number of users, and service requirements. For example, for small offices with limited space and a relatively small number of users, the cassette OLT, with its compact design and convenient installation, is an ideal choice. For large enterprises or data centers, the rack-mount OLT, with its robust scalability and high performance, can meet the needs of large-scale user access and complex service processing.
Core Function: Building an Efficient Network Hub
The core function of the OLT is to connect downstream optical network units (ONUs) and numerous user-side devices via optical fiber, enabling the aggregation, scheduling, and management of high-speed data, voice, video, and other services. Like an intelligent transportation hub, it integrates and distributes information flows from various directions in an orderly manner, ensuring efficient and stable transmission of various services.
Optical-Electrical Conversion: Bridging Network Transmission
Optical-electrical conversion is a fundamental function of the OLT, enabling efficient interoperability between optical and IP networks. During optical fiber transmission, information is transmitted in the form of optical signals, while user-side devices typically use electrical signals. The OLT accurately converts optical signals into electrical signals, enabling user-side devices to properly receive and process information. It also converts electrical signals from user-side devices into optical signals for long-distance, high-speed transmission via optical fiber. This efficient optical-to-electrical conversion ensures seamless connection of network signals between different media, providing a solid foundation for high-speed data transmission.
PON Technology: A Powerful Tool for Reducing Cabling Costs
PON technology (passive optical network) is a major highlight of OLTs. It covers a large number of users with a single optical fiber, significantly reducing cabling costs. Traditional network cabling methods require laying separate optical fibers for each user, which is both costly and complex. PON technology, on the other hand, utilizes a point-to-multipoint topology, using optical splitters to distribute the optical signal from a single fiber to multiple users, enabling resource sharing and efficient utilization. This technology not only reduces fiber usage and material costs, but also simplifies cabling projects and shortens construction cycles, saving businesses and organizations significant money and time.
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA): Intelligently Allocating Network Resources
Different users and services have varying bandwidth requirements during network usage. For example, video conferencing requires higher bandwidth to ensure clear and smooth video, while standard web browsing has lower bandwidth requirements. The OLT's Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) function intelligently allocates bandwidth resources based on the QoS (Quality of Service) priorities of different users and services. When a user or service requires more bandwidth, DBA automatically adjusts bandwidth allocation to ensure it has sufficient resources. When demand decreases, excess bandwidth is allocated to other users or services in need. This intelligent bandwidth allocation mechanism improves network resource utilization and ensures stable and efficient service for all services.
ONU Authentication and User Isolation: A Shield to Protect Network Security
Network security is a critical component of network construction. The OLT provides strong protection for secure network access through ONU authentication and user isolation. ONU authentication requires that each ONU connected to the network undergo strict identity verification. Only authenticated devices are allowed access, effectively preventing unauthorized access and minimizing the risk of network attacks and data leaks. Furthermore, user isolation isolates data from different users, preventing cross-data interference and ensuring that each user can access network services in an independent and secure environment.
Remote Management and Troubleshooting: Key to Reducing Operation and Maintenance Costs
For network operators, timely and efficient management and troubleshooting of network issues is crucial to ensuring normal network operation. The OLT features remote management and troubleshooting capabilities, allowing operators to configure, monitor, and manage the OLT remotely over the network without having to be physically present. When a network fault occurs, the OLT automatically detects and reports the fault information, allowing operators to quickly locate the cause and take appropriate measures to resolve it. This remote management and troubleshooting capability significantly reduces operation and maintenance costs, improves troubleshooting efficiency, and ensures network service quality.
Leading the New Trend in Network Development
With the continuous development of emerging technologies such as 5G, the Internet of Things, and cloud computing, network application scenarios will become increasingly diverse, placing higher demands on network speed, stability, and security. As the core equipment of passive optical local area networks (PLANs), the OLT will continue to undergo technological innovation and functional upgrades to meet the demands of future network development.
In the future, OLTs may have higher bandwidth processing capabilities and support higher-speed PON technologies such as 10G PON and 50G PON, providing users with an even faster network experience. At the same time, it will also strengthen integration with technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data, enabling more intelligent network management and optimization, and improving network adaptability and service quality.
With its powerful functionality and wide adaptability, the optical line terminal (OLT) plays an irreplaceable role in network construction in scenarios such as campuses, hotels, and enterprise LANs. It is not only the core engine of passive optical LANs but also a vital force driving the development of network technology. With continuous technological advancement, the OLT will continue to lead new trends in network development, creating a faster, more stable, and more secure network world.
Adapting to Diverse Scenarios and Flexibly Building POL Networks
With its exceptional adaptability, the OLT is widely applicable to OLT deployment in various environments, including campuses, hotels, and enterprise LANs. Whether it's a vibrant campus that needs to meet the diverse network needs of teachers and students for teaching, research, and entertainment; a warm and comfortable hotel that provides guests with smooth online services and a convenient smart experience; or an efficient enterprise LAN that ensures internal communications and efficient business operations, the OLT can handle it with ease.
It supports GPON/XG(s) PON technology, providing users with a variety of options. Available in both cassette and rack-mount form factors, this flexible design allows customers to tailor their POL networking solutions to their specific needs, such as site size, number of users, and service requirements. For example, for small offices with limited space and a relatively small number of users, the cassette OLT, with its compact design and convenient installation, is an ideal choice. For large enterprises or data centers, the rack-mount OLT, with its robust scalability and high performance, can meet the needs of large-scale user access and complex service processing.
Core Function: Building an Efficient Network Hub
The core function of the OLT is to connect downstream optical network units (ONUs) and numerous user-side devices via optical fiber, enabling the aggregation, scheduling, and management of high-speed data, voice, video, and other services. Like an intelligent transportation hub, it integrates and distributes information flows from various directions in an orderly manner, ensuring efficient and stable transmission of various services.
Optical-Electrical Conversion: Bridging Network Transmission
Optical-electrical conversion is a fundamental function of the OLT, enabling efficient interoperability between optical and IP networks. During optical fiber transmission, information is transmitted in the form of optical signals, while user-side devices typically use electrical signals. The OLT accurately converts optical signals into electrical signals, enabling user-side devices to properly receive and process information. It also converts electrical signals from user-side devices into optical signals for long-distance, high-speed transmission via optical fiber. This efficient optical-to-electrical conversion ensures seamless connection of network signals between different media, providing a solid foundation for high-speed data transmission.
PON Technology: A Powerful Tool for Reducing Cabling Costs
PON technology (passive optical network) is a major highlight of OLTs. It covers a large number of users with a single optical fiber, significantly reducing cabling costs. Traditional network cabling methods require laying separate optical fibers for each user, which is both costly and complex. PON technology, on the other hand, utilizes a point-to-multipoint topology, using optical splitters to distribute the optical signal from a single fiber to multiple users, enabling resource sharing and efficient utilization. This technology not only reduces fiber usage and material costs, but also simplifies cabling projects and shortens construction cycles, saving businesses and organizations significant money and time.
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA): Intelligently Allocating Network Resources
Different users and services have varying bandwidth requirements during network usage. For example, video conferencing requires higher bandwidth to ensure clear and smooth video, while standard web browsing has lower bandwidth requirements. The OLT's Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) function intelligently allocates bandwidth resources based on the QoS (Quality of Service) priorities of different users and services. When a user or service requires more bandwidth, DBA automatically adjusts bandwidth allocation to ensure it has sufficient resources. When demand decreases, excess bandwidth is allocated to other users or services in need. This intelligent bandwidth allocation mechanism improves network resource utilization and ensures stable and efficient service for all services.
ONU Authentication and User Isolation: A Shield to Protect Network Security
Network security is a critical component of network construction. The OLT provides strong protection for secure network access through ONU authentication and user isolation. ONU authentication requires that each ONU connected to the network undergo strict identity verification. Only authenticated devices are allowed access, effectively preventing unauthorized access and minimizing the risk of network attacks and data leaks. Furthermore, user isolation isolates data from different users, preventing cross-data interference and ensuring that each user can access network services in an independent and secure environment.
Remote Management and Troubleshooting: Key to Reducing Operation and Maintenance Costs
For network operators, timely and efficient management and troubleshooting of network issues is crucial to ensuring normal network operation. The OLT features remote management and troubleshooting capabilities, allowing operators to configure, monitor, and manage the OLT remotely over the network without having to be physically present. When a network fault occurs, the OLT automatically detects and reports the fault information, allowing operators to quickly locate the cause and take appropriate measures to resolve it. This remote management and troubleshooting capability significantly reduces operation and maintenance costs, improves troubleshooting efficiency, and ensures network service quality.
Leading the New Trend in Network Development
With the continuous development of emerging technologies such as 5G, the Internet of Things, and cloud computing, network application scenarios will become increasingly diverse, placing higher demands on network speed, stability, and security. As the core equipment of passive optical local area networks (PLANs), the OLT will continue to undergo technological innovation and functional upgrades to meet the demands of future network development.
In the future, OLTs may have higher bandwidth processing capabilities and support higher-speed PON technologies such as 10G PON and 50G PON, providing users with an even faster network experience. At the same time, it will also strengthen integration with technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data, enabling more intelligent network management and optimization, and improving network adaptability and service quality.
With its powerful functionality and wide adaptability, the optical line terminal (OLT) plays an irreplaceable role in network construction in scenarios such as campuses, hotels, and enterprise LANs. It is not only the core engine of passive optical LANs but also a vital force driving the development of network technology. With continuous technological advancement, the OLT will continue to lead new trends in network development, creating a faster, more stable, and more secure network world.